Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Its Origins
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized form of therapy that focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is a goal-oriented and evidence-based approach that helps individuals identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior to improve their emotional well-being.
The Development of CBT
CBT was developed in the 1960s by Aaron T. Beck, a psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, who initially intended to use it as a treatment for depression. However, Beck found that by challenging and changing negative thoughts, his patients experienced significant improvements not only in their mood but also in their overall functioning.
Beck’s groundbreaking work led to the development of cognitive therapy, which later evolved into cognitive behavioral therapy. He believed that our thoughts, rather than external events, influence our emotions and behaviors. By identifying and modifying these distorted thoughts, individuals can change their emotional responses and actions.
The History of CBT
Since its inception, CBT has gained recognition and popularity as an effective treatment for a wide range of mental health conditions. Over the years, it has been extensively researched and refined, making it one of the most widely practiced forms of therapy today.
In the 1970s and 1980s, other prominent psychologists, such as Albert Ellis and Donald Meichenbaum, made significant contributions to the development and application of CBT. Ellis developed Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), which focuses on challenging and changing irrational beliefs that contribute to emotional distress. Meichenbaum introduced Cognitive Behavioral Modification (CBM), which emphasizes the role of self-instructional training in changing behavior.
CBT gained further recognition in the 1990s when it was endorsed by various professional organizations and included in treatment guidelines for numerous mental health disorders. Its effectiveness has been supported by extensive research and clinical studies, demonstrating its efficacy in treating conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, eating disorders, substance abuse, and many others.
The Core Principles of CBT
CBT is based on several core principles that guide the therapeutic process:
- Collaborative Approach: CBT is a collaborative effort between the therapist and the individual seeking treatment. They work together to identify and address specific goals.
- Present-Focused: CBT primarily focuses on the present rather than delving extensively into past experiences. It aims to help individuals understand and change their current thoughts and behaviors.
- Thought-Behavior Connection: CBT recognizes the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By identifying and challenging negative thoughts, individuals can change their emotional responses and behaviors.
- Evidence-Based Techniques: CBT utilizes evidence-based techniques and strategies that have been proven effective in scientific research. These techniques may include cognitive restructuring, behavioral experiments, and problem-solving skills.
- Homework and Practice: CBT often involves assigning homework and encouraging individuals to practice new skills outside of therapy sessions. This helps reinforce learning and facilitates lasting change.
CBT is a flexible and adaptable therapy that can be tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. It empowers individuals to take an active role in their treatment and provides them with practical tools to manage their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has a rich history and continues to be a widely utilized and effective form of therapy. Developed by Aaron T. Beck, CBT focuses on the connection between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Over the years, it has evolved and expanded, incorporating contributions from other influential psychologists. CBT’s core principles and evidence-based techniques make it a valuable tool in helping individuals overcome various mental health challenges and improve their overall well-being.
Learn More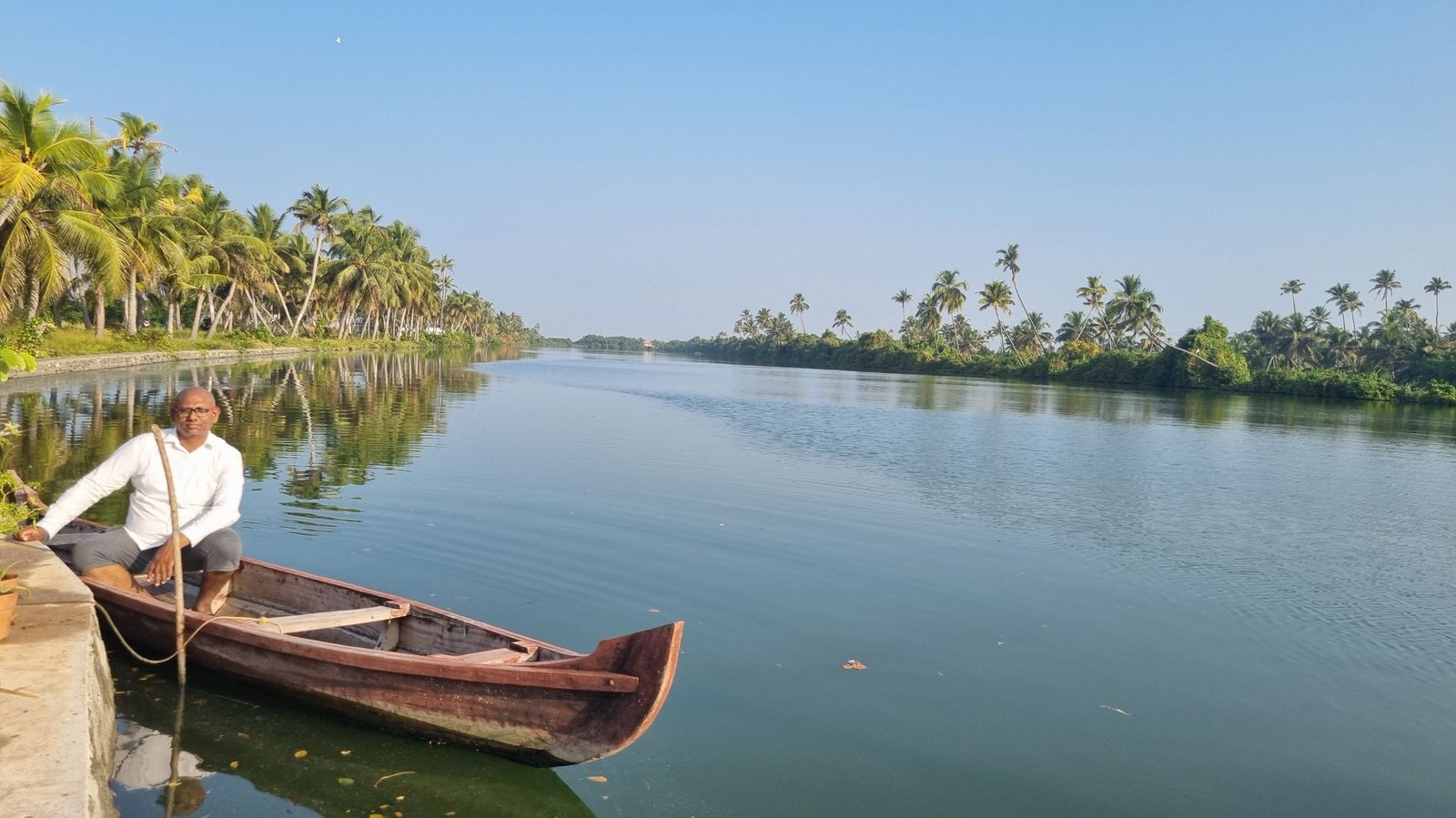
The Art of Shinrin Yoku and the Benefits of Boat Therapy
Shinrin Yoku, also known as forest bathing, and boat therapy are two unique practices that offer incredible benefits for our mental and physical well-being. In today’s fast-paced and stressful world, finding ways to reconnect with nature and promote relaxation is more important than ever. Let’s explore what these practices entail and the advantages they bring.
Shinrin Yoku: The Healing Power of Forest Bathing
Shinrin Yoku is a Japanese term that translates to “forest bathing.” It involves immersing oneself in the natural environment of a forest, taking in the sights, sounds, and smells. This practice goes beyond just hiking or walking in the woods; it is about mindfully connecting with nature and allowing it to heal and rejuvenate us.
When engaging in Shinrin Yoku, the focus is on being present and fully experiencing the forest. This can involve activities such as meditating, breathing exercises, or simply sitting quietly and observing the surroundings. The goal is to awaken our senses and create a deep connection with the natural world.
Research has shown that Shinrin Yoku offers numerous benefits for our well-being. Spending time in nature has been found to reduce stress levels, lower blood pressure, and boost the immune system. It can also improve mood, increase creativity, and enhance concentration and focus. The phytoncides, or essential oils released by trees, have been found to have a positive impact on our immune system, further contributing to our overall health.
Boat Therapy: Serenity on the Water
Boat therapy, on the other hand, is a practice that involves spending time on a boat, whether it’s a sailboat, kayak, or any other type of water vessel. Being on the water can have a calming effect on our minds and bodies, providing a unique sense of serenity and tranquility.
One of the main benefits of boat therapy is the opportunity to disconnect from the noise and distractions of everyday life. When we are on a boat, surrounded by water and away from the hustle and bustle of the city, we can find a sense of peace and solitude. This can help us relax, reduce anxiety, and improve our overall mental well-being.
Boat therapy also offers physical benefits. Engaging in activities such as rowing or sailing can provide a low-impact workout that improves cardiovascular health and strengthens muscles. The gentle rocking motion of the boat can have a soothing effect on our bodies, promoting relaxation and better sleep.
The Overlapping Benefits
While Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy are distinct practices, they share some common benefits. Both allow us to reconnect with nature and tap into its healing power. They offer an escape from the stresses of daily life and provide an opportunity to slow down and appreciate the beauty of our surroundings.
Engaging in these practices can also help improve our mental clarity and focus. By taking a break from technology and the constant demands of work, we can give our minds a chance to rest and recharge. This can lead to increased productivity and creativity when we return to our daily tasks.
Furthermore, both Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy encourage mindfulness and being present in the moment. They teach us to appreciate the small details of our environment and find joy in the simplicity of nature. This mindfulness can extend beyond our time in the forest or on the water, positively impacting our overall outlook on life.
Conclusion
Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy are powerful practices that offer numerous benefits for our well-being. Whether we choose to immerse ourselves in the tranquility of a forest or find solace on the water, these practices allow us to reconnect with nature and find inner peace. By incorporating these activities into our lives, we can experience improved mental and physical health, reduced stress levels, and a deeper appreciation for the beauty of the natural world.
Learn More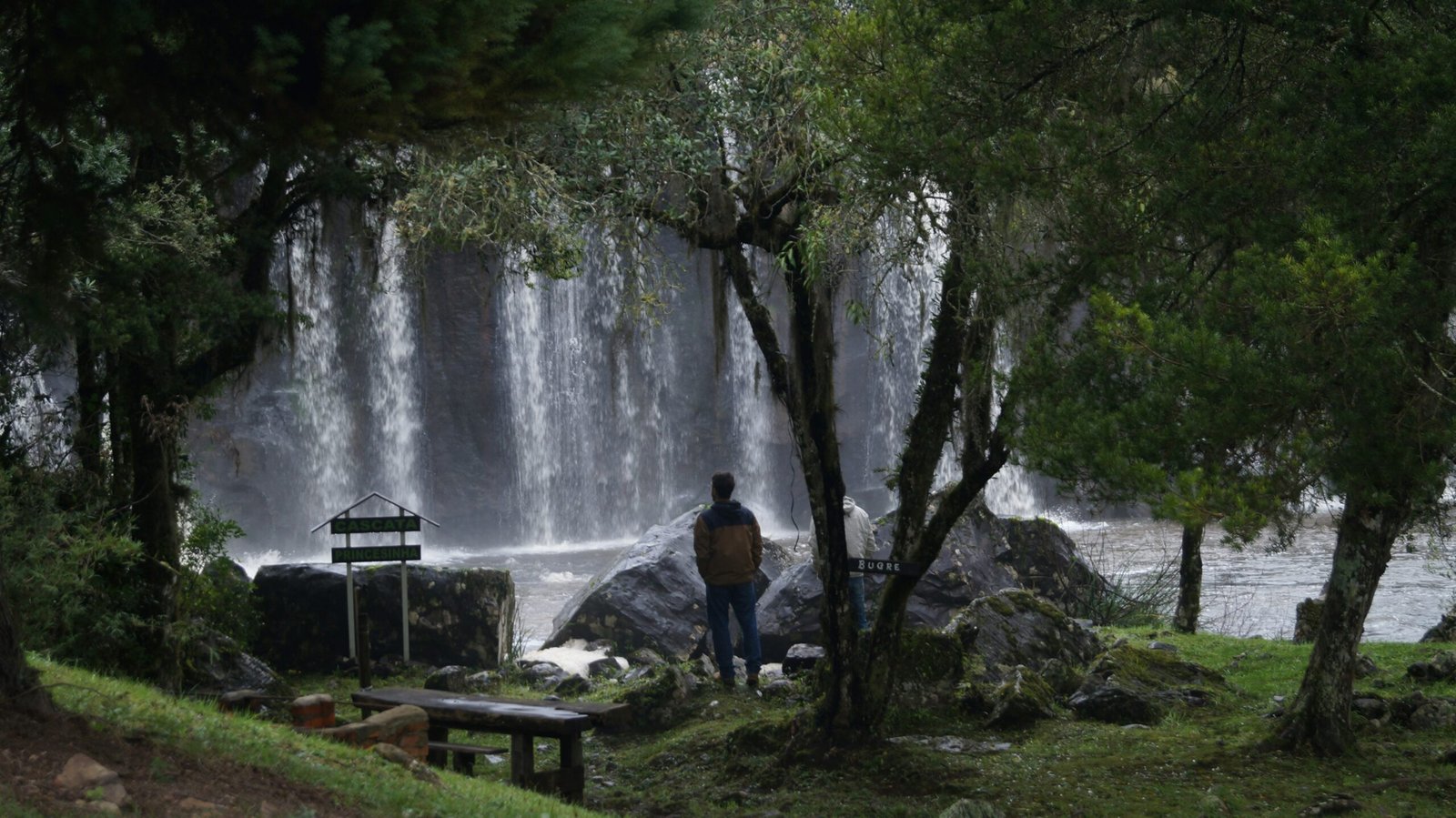
The Art of Shinrin Yoku and the Benefits of Boat Therapy
Shinrin Yoku, also known as forest bathing, and boat therapy are two unique practices that offer incredible benefits for our mental and physical well-being. In today’s fast-paced and stressful world, finding ways to reconnect with nature and promote relaxation is more important than ever. Let’s explore what these practices entail and the advantages they bring.
Shinrin Yoku: The Healing Power of Forest Bathing
Shinrin Yoku is a Japanese term that translates to “forest bathing.” It involves immersing oneself in the natural environment of a forest, taking in the sights, sounds, and smells. This practice goes beyond just hiking or walking in the woods; it is about mindfully connecting with nature and allowing it to heal and rejuvenate us.
When engaging in Shinrin Yoku, the focus is on being present and fully experiencing the forest. This can involve activities such as meditating, breathing exercises, or simply sitting quietly and observing the surroundings. The goal is to awaken our senses and create a deep connection with the natural world.
Research has shown that Shinrin Yoku offers numerous benefits for our well-being. Spending time in nature has been found to reduce stress levels, lower blood pressure, and boost the immune system. It can also improve mood, increase creativity, and enhance concentration and focus. The phytoncides, or essential oils released by trees, have been found to have a positive impact on our immune system, further contributing to our overall health.
Boat Therapy: Serenity on the Water
Boat therapy, on the other hand, is a practice that involves spending time on a boat, whether it’s a sailboat, kayak, or any other type of water vessel. Being on the water can have a calming effect on our minds and bodies, providing a unique sense of serenity and tranquility.
One of the main benefits of boat therapy is the opportunity to disconnect from the noise and distractions of everyday life. When we are on a boat, surrounded by water and away from the hustle and bustle of the city, we can find a sense of peace and solitude. This can help us relax, reduce anxiety, and improve our overall mental well-being.
Boat therapy also offers physical benefits. Engaging in activities such as rowing or sailing can provide a low-impact workout that improves cardiovascular health and strengthens muscles. The gentle rocking motion of the boat can have a soothing effect on our bodies, promoting relaxation and better sleep.
The Overlapping Benefits
While Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy are distinct practices, they share some common benefits. Both allow us to reconnect with nature and tap into its healing power. They offer an escape from the stresses of daily life and provide an opportunity to slow down and appreciate the beauty of our surroundings.
Engaging in these practices can also help improve our mental clarity and focus. By taking a break from technology and the constant demands of work, we can give our minds a chance to rest and recharge. This can lead to increased productivity and creativity when we return to our daily tasks.
Furthermore, both Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy encourage mindfulness and being present in the moment. They teach us to appreciate the small details of our environment and find joy in the simplicity of nature. This mindfulness can extend beyond our time in the forest or on the water, positively impacting our overall outlook on life.
Conclusion
Shinrin Yoku and boat therapy are powerful practices that offer numerous benefits for our well-being. Whether we choose to immerse ourselves in the tranquility of a forest or find solace on the water, these practices allow us to reconnect with nature and find inner peace. By incorporating these activities into our lives, we can experience improved mental and physical health, reduced stress levels, and a deeper appreciation for the beauty of the natural world.
Learn More
Understanding Sex Education for Couples
What is Sex Education for Couples?
Sex education for couples refers to the process of providing information and guidance on sexual health, intimacy, and relationships to individuals in committed partnerships. It aims to enhance communication, understanding, and satisfaction between partners, ultimately leading to a healthier and more fulfilling sexual relationship.
The Benefits of Sex Education for Couples
Engaging in sex education as a couple can have numerous benefits for both partners. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Communication: Sex education encourages open and honest communication between partners, allowing them to express their desires, concerns, and boundaries more effectively.
- Enhanced Intimacy: By understanding each other’s needs and preferences, couples can deepen their emotional and physical connection, leading to a more satisfying and intimate relationship.
- Increased Sexual Satisfaction: Sex education equips couples with knowledge and techniques to enhance sexual pleasure, leading to greater satisfaction for both partners.
- Reduced Anxiety and Stress: Learning about sexual health and exploring concerns together can help alleviate anxiety and stress related to sexual performance or intimacy issues.
- Prevention of Sexual Problems: Sex education can help couples identify and address potential sexual problems early on, preventing them from escalating and negatively impacting the relationship.
How to Approach Sex Education for Couples
Approaching sex education as a couple requires sensitivity, respect, and a willingness to learn and grow together. Here are some tips to help you navigate this process:
- Establish Trust: Create a safe and non-judgmental space where both partners feel comfortable discussing their feelings, desires, and concerns.
- Start with Open Communication: Initiate conversations about sexual health and intimacy by expressing your own thoughts and feelings, and encourage your partner to do the same.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider attending workshops or seeking guidance from a certified sex therapist who can provide expert advice and support tailored to your specific needs.
- Explore Together: Engage in activities such as reading books, watching educational videos, or attending seminars together to expand your knowledge and understanding of sexuality.
- Experiment and Discover: Embrace a spirit of exploration and curiosity, trying new things and discovering what brings pleasure and satisfaction to both partners.
Common Sexual Concerns for Couples
Sexual concerns can arise in any relationship, and addressing them openly can lead to resolution and growth. Here are some common sexual concerns couples may face:
- Lack of desire or mismatched libido
- Difficulty with arousal or achieving orgasm
- Communication issues around sexual needs and preferences
- Performance anxiety or erectile dysfunction
- Pain or discomfort during sex
Signs of a Healthy Sex Life
A healthy sex life is characterized by open communication, mutual consent, and satisfaction for both partners. Here are some signs of a healthy sexual relationship:
- Regular and enjoyable sexual activity
- Respect for each other’s boundaries and desires
- Willingness to explore and try new things together
- Emotional intimacy and connection
- Ability to discuss and address concerns or issues openly
15 Tips for a Healthy Sex Life
Here are some practical tips to help you maintain a healthy and fulfilling sex life:
- Communicate openly and honestly about your desires and boundaries.
- Make time for intimacy and prioritize it in your relationship.
- Explore each other’s bodies and discover what brings pleasure.
- Practice active consent and respect each other’s choices.
- Engage in foreplay and build anticipation before sexual activity.
- Experiment with different positions and techniques to find what works best for you.
- Take care of your sexual health by practicing safe sex and getting regular check-ups.
- Manage stress and prioritize self-care to maintain a healthy libido.
- Stay physically active to improve overall energy and stamina.
- Use lubrication if needed to enhance comfort and pleasure.
- Address any underlying relationship issues that may be affecting your sexual connection.
- Stay curious and open-minded about sexuality and its possibilities.
- Continue learning and educating yourselves about sexual health and pleasure.
- Celebrate and appreciate each other’s bodies and sexual identities.
- Remember that sexual satisfaction and fulfillment can evolve and change over time, so be adaptable and open to new experiences.
By investing in sex education as a couple, you can strengthen your bond, deepen your intimacy, and create a fulfilling and satisfying sexual relationship.
Learn More
What is CBT? A Comprehensive Guide to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
-CLICK HERE TO LISTEN-NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CBT – AUDIO SELF -HELP SERIES
Introduction
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, commonly known as CBT, is a widely recognized and effective form of psychotherapy. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to emotional distress. By addressing these patterns, CBT helps individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and achieve better mental well-being.
How Does CBT Work?
CBT operates on the principle that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. It recognizes that distorted or negative thoughts can influence our emotions and actions, leading to a cycle of negative experiences. The goal of CBT is to help individuals break this cycle by challenging and replacing negative thoughts with more realistic and positive ones.
Key Concepts in CBT
CBT is based on several core principles and techniques:
- Cognitive Restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and replacing them with more rational and balanced thoughts.
- Behavioral Activation: By engaging in positive behaviors and activities, individuals can experience an improvement in their mood and overall well-being.
- Exposure Therapy: This technique involves gradually exposing individuals to situations or stimuli that trigger anxiety or fear, helping them confront and overcome their fears.
- Skills Training: CBT often includes teaching individuals specific skills, such as problem-solving and stress management, to help them better cope with challenges.
How Can CBT Help?
CBT has been proven effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Substance abuse
- Eating disorders
- Insomnia
It can also be helpful for individuals experiencing relationship difficulties, low self-esteem, and stress-related problems.
CBT Self-Help Resources
If you are interested in exploring CBT further or would like to try some self-help techniques, the following resources can be a valuable starting point:
- NHS Self-Help Therapies: The National Health Service (NHS) provides a range of self-help resources for various mental health conditions, including CBT-based interventions.
- Moodjuice: This website offers self-help resources, worksheets, and interactive tools based on CBT principles to help individuals manage their mental health.
- Psychology Tools: Psychology Tools provides a wide range of free CBT worksheets and resources for therapists and individuals seeking self-help.
- Get Self Help: This website offers free CBT self-help resources, including worksheets, information leaflets, and audio recordings.
While self-help resources can be beneficial, it is important to note that CBT is most effective when delivered by a trained therapist. If you are struggling with significant mental health challenges, it is recommended to seek professional help.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a powerful therapeutic approach that can help individuals overcome negative thoughts and behaviors and improve their mental well-being. By challenging and replacing negative thoughts, individuals can break the cycle of distress and develop healthier coping mechanisms. While self-help resources can be valuable, working with a trained therapist is often the most effective way to experience the full benefits of CBT.
Learn MoreUnderstanding Fillicide: Causes, Notable Cases, and Preventive Measures
PPT ON SUCHANA SETH-A PSYCHOLOGICAL PERVIEW- CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD
Introduction
Fillicide, the act of a parent killing their own child, is a tragic and deeply disturbing phenomenon that has occurred throughout history. This blog post aims to shed light on the concept of fillicide, explore its underlying reasons, examine notable cases, and discuss the importance of mental health in preventing such acts.
Suchana Seth, CEO of artificial intelligence start-up Mindful AI Lab, was arrested in Karnataka’s Chitradurga with her son’s body in a bag.
Bengaluru-based artificial intelligence start-up CEO was arrested by Karnataka Police on Monday when she tried to flee with the body of her 4-year-old son.
Suchana Seth, 39, allegedly killed her son at a Goa hotel and was fleeing to Karnataka in a taxi with the body stuffed in a bag. However, police got the whiff of the incident and arrested Seth from Karnataka’s Chitradurga.
The Mindful AI Lab CEO had checked in a Goa hotel on January 6 and checked out two days later on January 8.
The incident came to light after a hotel staff noticed blood stains in the room where Seth had stayed, and alerted the police.
According to the police, after committing the crime, Suchana Seth had asked the hotel staff to arrange a taxi for her.
When police confronted her, she told them that she had left her son at a relative’s place in South Goa. The address she gave became fake. Police found her answers evasive and they got suspicious. They asked the cab driver to report to the police station to gather more information. During interrogation, they found the body of the four years boy in the suitcasse.
Understanding Fillicide
Fillicide is a term derived from the Latin words “filii” (child) and “cidium” (killing). It refers to the intentional act of a parent taking the life of their own biological or adopted child. This act can occur in various forms, including infanticide (killing of an infant), neonaticide (killing of a newborn), or even the murder of an adult child.
Reasons for Fillicide
Understanding the complex motivations behind fillicide is crucial in order to address and prevent such tragic events. While each case is unique, several common factors have been identified:
1. Mental Health Issues: Mental health problems, such as postpartum depression, psychosis, or other psychiatric disorders, can significantly contribute to the occurrence of fillicide. These conditions may impair a parent’s judgment, distort their perception of reality, or lead to a loss of emotional control.
2. Relationship Problems: Strained relationships between parents, marital conflicts, or custody disputes can create an environment of extreme stress and emotional turmoil. These factors, when combined with unresolved anger or resentment, may increase the risk of fillicide.
3. Substance Abuse: Substance abuse, including alcohol and drug addiction, can impair judgment, alter behavior, and contribute to violent tendencies. Parents struggling with addiction may become neglectful, abusive, or even resort to fillicide.
4. Financial Stress: Financial difficulties, such as unemployment, debt, or poverty, can create immense pressure on parents. The inability to provide for their child’s basic needs may lead to feelings of hopelessness, desperation, and, in extreme cases, fillicide.
Famous Fillicide Cases
While every fillicide case is a tragedy, some have gained significant media attention due to their shocking nature or high-profile individuals involved. Notable examples include:
1. Andrea Yates: In 2001, Andrea Yates drowned her five children in a bathtub. She suffered from severe postpartum depression and psychosis, highlighting the importance of recognizing and treating mental health issues.
2. Susan Smith: In 1994, Susan Smith strapped her two young sons into their car seats and rolled the car into a lake, resulting in their deaths. Smith’s actions were driven by a desire to pursue a relationship without the burden of motherhood.
3. Mary Ann Cotton: In the 19th century, Mary Ann Cotton poisoned several of her children and stepchildren for financial gain. Her case exemplifies the intersection of financial stress and fillicide.
Mental Health and Fillicide Prevention
To effectively prevent fillicide, addressing mental health issues is of paramount importance. This can be achieved through various means:
1. Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about the signs and symptoms of mental health disorders, particularly those affecting parents, can help identify individuals at risk and facilitate early intervention.
2. Access to Mental Health Services: Ensuring accessible and affordable mental health services, including therapy and counseling, can provide parents with the support they need to manage their mental well-being and prevent potential acts of fillicide.
3. Supportive Parenting Programs: Implementing programs that promote positive parenting skills, stress management techniques, and conflict resolution can help parents navigate the challenges they may face, reducing the likelihood of fillicide.
4. Encouraging Help-Seeking Behavior: Reducing the stigma associated with mental health issues and encouraging parents to seek help when needed can contribute to early intervention and prevention of fillicide.
Conclusion
Fillicide is a tragic and complex phenomenon that demands our attention and understanding. By addressing the underlying causes, promoting mental health awareness, and providing support to parents, we can strive towards a society where fillicide becomes a thing of the past. Let us work together to create a safer and more compassionate world for children and their families.
Emotional Intelligence and Basic psychology is to be taught to everyone. Kindly get in touch with Emocare, India’s first chain of counselling centers to learn Psychology or to take Effective Internship in Psychology. Please download a PPT on the issue.
NATIONAL LIBRARY OF MEDICINE-CASE STUDY ON FILICIDE
FILICIDE- WHAT MENTAL HEALTH PRACTITIONERS SHOULD KNOW
Learn More
Understanding Sexual Dysfunction and the Benefits of Sex Therapy
Introduction
Sexual dysfunction is a common issue that can affect individuals and couples of all ages. It refers to a range of problems that prevent a person from experiencing satisfaction or pleasure during sexual activity. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of sexual dysfunction, the symptoms to look out for, and the benefits of seeking sex therapy.
What is Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction encompasses a variety of conditions that can affect both men and women. It can manifest as a lack of desire, difficulty achieving or maintaining arousal, pain during intercourse, or an inability to achieve orgasm. These issues can cause significant distress and strain on relationships if left unaddressed.
Types of Sexual Dysfunction
There are several types of sexual dysfunction, including:
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection in men.
- Premature Ejaculation: Ejaculating too quickly before or shortly after penetration.
- Delayed Ejaculation: Difficulty or inability to ejaculate, despite adequate stimulation.
- Female Sexual Arousal Disorder: Difficulty achieving or maintaining arousal in women.
- Orgasmic Disorder: Difficulty reaching orgasm or a lack of orgasmic intensity.
- Dyspareunia: Persistent pain during sexual intercourse.
- Vaginismus: Involuntary muscle spasms that make penetration painful or impossible.
Who is Affected by Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction can affect individuals of any gender, age, or sexual orientation. It is estimated that up to 43% of women and 31% of men experience some form of sexual dysfunction at some point in their lives. It is important to note that sexual dysfunction is not a reflection of one’s attractiveness or desirability, but rather a complex interplay of physical, psychological, and relational factors.
Sexual Trauma
Sexual trauma, such as past abuse or assault, can contribute to the development of sexual dysfunction. Traumatic experiences can lead to feelings of fear, shame, and anxiety, making it challenging to engage in healthy sexual relationships. Sex therapy can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to address and heal from past traumas.
Symptoms of Sexual Dysfunction
The symptoms of sexual dysfunction can vary depending on the specific condition but may include:
- Lack of sexual desire or interest
- Difficulty becoming aroused
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse
- Inability to achieve orgasm
- Feeling distressed or dissatisfied with one’s sexual experiences
What to Expect from Sex Therapy
Sex therapy is a specialized form of therapy that focuses on addressing sexual concerns and improving sexual functioning. During sex therapy sessions, a trained therapist will work with individuals or couples to explore the underlying causes of their sexual dysfunction and develop strategies for improvement. This may involve communication exercises, education about sexual anatomy and response, and the use of techniques to reduce anxiety and increase pleasure.
Causes of Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction can have both physical and psychological causes. Physical causes may include hormonal imbalances, certain medications, chronic illnesses, or neurological conditions. Psychological causes can include stress, anxiety, depression, body image issues, relationship problems, or a history of trauma. A comprehensive assessment by a sex therapist can help identify the underlying factors contributing to sexual dysfunction.
Couples Sex Therapy
Sexual dysfunction can have a significant impact on a couple’s relationship. Couples sex therapy provides a space for partners to address their concerns together and work towards improving their sexual connection. Through open communication, couples can learn to express their needs, deepen intimacy, and develop strategies to overcome sexual challenges as a team.
Finding a Sex Therapist
When seeking sex therapy, it is crucial to find a qualified and experienced sex therapist. Look for therapists who have specialized training in sex therapy and are certified by reputable organizations. It is also important to find a therapist with whom you feel comfortable and can trust to create a safe and non-judgmental space for exploration and healing.
Conclusion
Sexual dysfunction is a common issue that can affect individuals and couples, but it is not something that has to be endured in silence. Sex therapy offers a path towards understanding and resolving sexual concerns, leading to improved sexual satisfaction and overall well-being. By seeking help from a trained professional, individuals and couples can overcome sexual challenges and cultivate a healthier and more fulfilling sexual life.
Learn More
Substance-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Understanding Diagnostic Features, Distinguishing Factors, and Treatment Options
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual functioning and overall quality of life. It occurs as a result of substance use or due to the side effects of certain medications. In this article, we will explore the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, specifiers, specific substances, and available treatments for substance-induced sexual dysfunction.
Diagnostic Features
When diagnosing substance-induced sexual dysfunction, medical professionals look for several key features. First, there must be evidence of clinically significant sexual dysfunction. This can include a decrease in sexual desire, arousal difficulties, orgasmic dysfunction, or sexual pain disorders. It is important to note that the sexual dysfunction should have started during or soon after substance use or medication initiation.
Second, there must be evidence that the substance or medication is capable of causing sexual dysfunction. This can be determined by the timing of the sexual dysfunction in relation to substance use or medication initiation, as well as by the presence of other adverse effects associated with the substance or medication.
Distinguishing Factors
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be distinguished from other sexual dysfunctions by its temporal relationship to substance use or medication initiation. Unlike other sexual dysfunctions, substance-induced sexual dysfunction is typically reversible and improves with abstinence from the substance or discontinuation of the medication. This distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
It’s also important to consider the specific substance or medication involved. Different substances can have varying effects on sexual functioning. For example, substances such as alcohol, opioids, and sedatives can depress sexual desire and impair sexual performance. Stimulants, on the other hand, may increase sexual desire but can lead to difficulties with arousal or orgasm.
Specifiers
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be further specified based on the severity and duration of the symptoms. Severity can range from mild to moderate to severe, depending on the impact on sexual functioning and overall distress. Duration can be specified as acute (less than six months) or persistent (six months or more).
Specific Substances
Various substances and medications have been associated with sexual dysfunction. Alcohol, opioids, sedatives, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antihypertensive medications are among the most common culprits. It’s important to note that not everyone who uses these substances or medications will experience sexual dysfunction, but it is a potential side effect that should be considered.
Treatments
The treatment of substance-induced sexual dysfunction involves addressing both the underlying substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself. The primary approach is to promote abstinence from the substance or switch to an alternative medication that is less likely to cause sexual dysfunction.
In addition to addressing the substance or medication, various therapies can be helpful in managing sexual dysfunction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs related to sexual performance. Couples therapy can improve communication and intimacy, which can positively impact sexual functioning. In some cases, medication such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra) may be prescribed to temporarily alleviate sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a significant concern for individuals who use substances or take certain medications. Understanding the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, and treatment options can help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage this condition. By addressing both the substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself, individuals can work towards improving their sexual functioning and overall well-being.
Learn More
Substance-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Understanding Diagnostic Features, Distinguishing Factors, and Treatment Options
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual functioning and overall quality of life. It occurs as a result of substance use or due to the side effects of certain medications. In this article, we will explore the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, specifiers, specific substances, and available treatments for substance-induced sexual dysfunction.
Diagnostic Features
When diagnosing substance-induced sexual dysfunction, medical professionals look for several key features. First, there must be evidence of clinically significant sexual dysfunction. This can include a decrease in sexual desire, arousal difficulties, orgasmic dysfunction, or sexual pain disorders. It is important to note that the sexual dysfunction should have started during or soon after substance use or medication initiation.
Second, there must be evidence that the substance or medication is capable of causing sexual dysfunction. This can be determined by the timing of the sexual dysfunction in relation to substance use or medication initiation, as well as by the presence of other adverse effects associated with the substance or medication.
Distinguishing Factors
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be distinguished from other sexual dysfunctions by its temporal relationship to substance use or medication initiation. Unlike other sexual dysfunctions, substance-induced sexual dysfunction is typically reversible and improves with abstinence from the substance or discontinuation of the medication. This distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
It’s also important to consider the specific substance or medication involved. Different substances can have varying effects on sexual functioning. For example, substances such as alcohol, opioids, and sedatives can depress sexual desire and impair sexual performance. Stimulants, on the other hand, may increase sexual desire but can lead to difficulties with arousal or orgasm.
Specifiers
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be further specified based on the severity and duration of the symptoms. Severity can range from mild to moderate to severe, depending on the impact on sexual functioning and overall distress. Duration can be specified as acute (less than six months) or persistent (six months or more).
Specific Substances
Various substances and medications have been associated with sexual dysfunction. Alcohol, opioids, sedatives, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antihypertensive medications are among the most common culprits. It’s important to note that not everyone who uses these substances or medications will experience sexual dysfunction, but it is a potential side effect that should be considered.
Treatments
The treatment of substance-induced sexual dysfunction involves addressing both the underlying substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself. The primary approach is to promote abstinence from the substance or switch to an alternative medication that is less likely to cause sexual dysfunction.
In addition to addressing the substance or medication, various therapies can be helpful in managing sexual dysfunction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs related to sexual performance. Couples therapy can improve communication and intimacy, which can positively impact sexual functioning. In some cases, medication such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra) may be prescribed to temporarily alleviate sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a significant concern for individuals who use substances or take certain medications. Understanding the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, and treatment options can help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage this condition. By addressing both the substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself, individuals can work towards improving their sexual functioning and overall well-being.
Learn More
Understanding Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder (GPPPD) is a condition that affects individuals, predominantly women, and can have a significant impact on their sexual well-being and overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for GPPPD.
Causes of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
GPPPD can have various underlying causes, both physical and psychological. Physical causes may include vaginal infections, hormonal imbalances, pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, or certain medical conditions. Psychological factors such as anxiety, fear, past traumatic experiences, or relationship issues can also contribute to the development of GPPPD.
Symptoms of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
The symptoms of GPPPD can manifest differently in each individual, but common symptoms include pain or discomfort during vaginal penetration, muscle spasms in the pelvic floor, fear or anxiety related to sexual activities, and avoidance of sexual intimacy. These symptoms can have a significant impact on sexual satisfaction and overall well-being.
Diagnosis of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
Diagnosing GPPPD requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, conduct a physical examination, and may recommend additional tests or consultations with specialists to rule out any underlying physical or psychological conditions. It is essential to establish an accurate diagnosis to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
Treating GPPPD often involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing both physical and psychological aspects of the condition. The treatment plan may include general measures, psychological therapies, or a combination of both.
General Measures
General measures aim to alleviate physical symptoms and promote overall sexual well-being. These may include:
– Lubricants: Using water-based lubricants during sexual activities can help reduce discomfort and improve sexual pleasure.
– Pelvic floor exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises, such as Kegels, can help improve muscle control and reduce pain.
– Education and counseling: Learning about GPPPD and receiving counseling can help individuals better understand their condition and develop coping strategies.
Psychological Therapies
Psychological therapies play a crucial role in addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of GPPPD. These therapies may include:
– Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs related to their condition, promoting healthier attitudes towards sex and intimacy.
– Mindfulness-based techniques: Techniques such as meditation and mindfulness can help individuals develop awareness and acceptance of their physical sensations, reducing anxiety and fear during sexual activities.
– Couples therapy: In cases where GPPPD affects the individual’s relationship, couples therapy can help improve communication, address relationship issues, and foster a supportive and understanding environment.
Conclusion
Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual well-being and overall quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for GPPPD, individuals can seek appropriate help and support. With the right interventions, it is possible to manage and overcome GPPPD, leading to a healthier and more satisfying sexual life.
Learn More