Substance-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Understanding Diagnostic Features, Distinguishing Factors, and Treatment Options
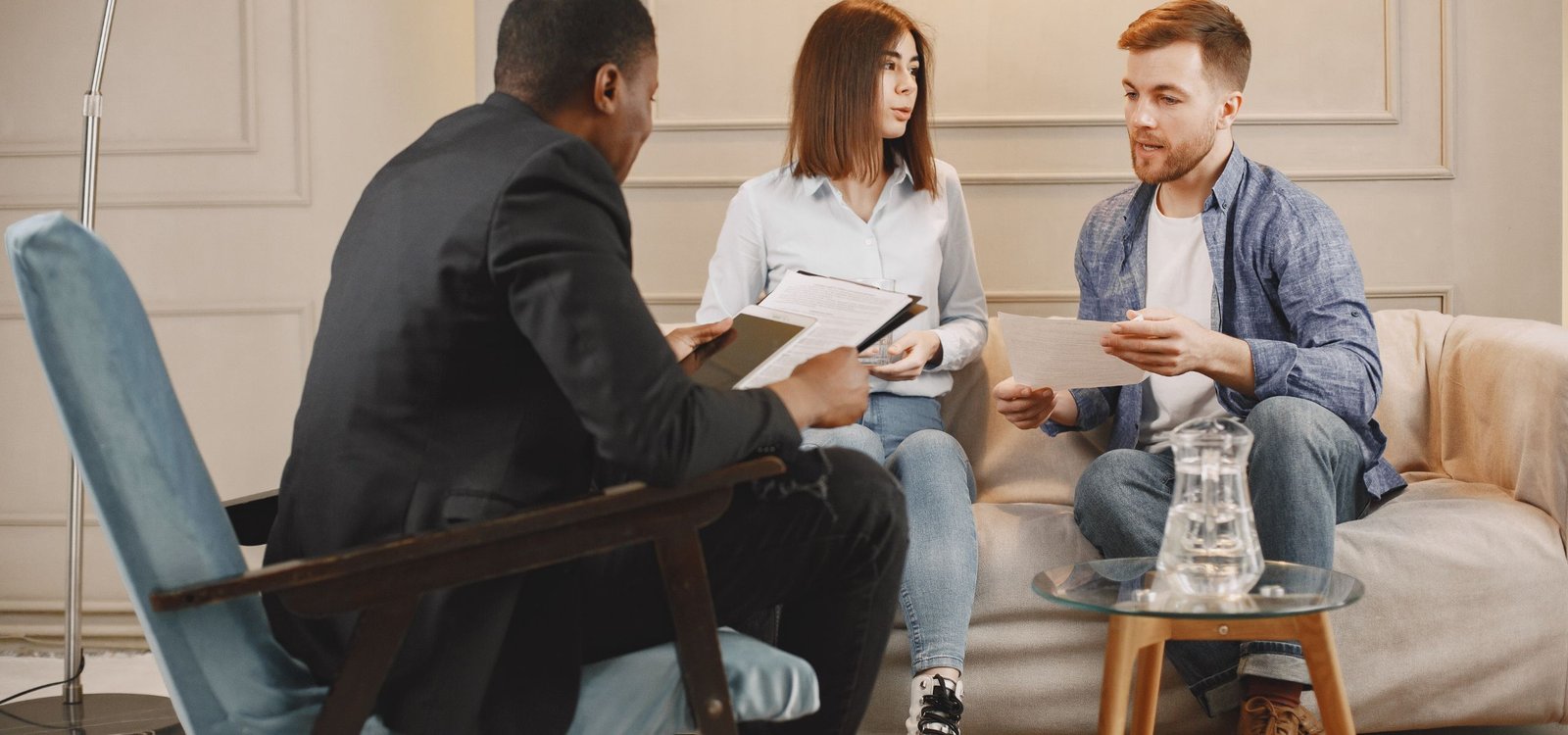
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual functioning and overall quality of life. It occurs as a result of substance use or due to the side effects of certain medications. In this article, we will explore the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, specifiers, specific substances, and available treatments for substance-induced sexual dysfunction.
Diagnostic Features
When diagnosing substance-induced sexual dysfunction, medical professionals look for several key features. First, there must be evidence of clinically significant sexual dysfunction. This can include a decrease in sexual desire, arousal difficulties, orgasmic dysfunction, or sexual pain disorders. It is important to note that the sexual dysfunction should have started during or soon after substance use or medication initiation.
Second, there must be evidence that the substance or medication is capable of causing sexual dysfunction. This can be determined by the timing of the sexual dysfunction in relation to substance use or medication initiation, as well as by the presence of other adverse effects associated with the substance or medication.
Distinguishing Factors
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be distinguished from other sexual dysfunctions by its temporal relationship to substance use or medication initiation. Unlike other sexual dysfunctions, substance-induced sexual dysfunction is typically reversible and improves with abstinence from the substance or discontinuation of the medication. This distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
It’s also important to consider the specific substance or medication involved. Different substances can have varying effects on sexual functioning. For example, substances such as alcohol, opioids, and sedatives can depress sexual desire and impair sexual performance. Stimulants, on the other hand, may increase sexual desire but can lead to difficulties with arousal or orgasm.
Specifiers
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be further specified based on the severity and duration of the symptoms. Severity can range from mild to moderate to severe, depending on the impact on sexual functioning and overall distress. Duration can be specified as acute (less than six months) or persistent (six months or more).
Specific Substances
Various substances and medications have been associated with sexual dysfunction. Alcohol, opioids, sedatives, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antihypertensive medications are among the most common culprits. It’s important to note that not everyone who uses these substances or medications will experience sexual dysfunction, but it is a potential side effect that should be considered.
Treatments
The treatment of substance-induced sexual dysfunction involves addressing both the underlying substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself. The primary approach is to promote abstinence from the substance or switch to an alternative medication that is less likely to cause sexual dysfunction.
In addition to addressing the substance or medication, various therapies can be helpful in managing sexual dysfunction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs related to sexual performance. Couples therapy can improve communication and intimacy, which can positively impact sexual functioning. In some cases, medication such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra) may be prescribed to temporarily alleviate sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a significant concern for individuals who use substances or take certain medications. Understanding the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, and treatment options can help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage this condition. By addressing both the substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself, individuals can work towards improving their sexual functioning and overall well-being.
Learn More
Substance-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Understanding Diagnostic Features, Distinguishing Factors, and Treatment Options
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual functioning and overall quality of life. It occurs as a result of substance use or due to the side effects of certain medications. In this article, we will explore the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, specifiers, specific substances, and available treatments for substance-induced sexual dysfunction.
Diagnostic Features
When diagnosing substance-induced sexual dysfunction, medical professionals look for several key features. First, there must be evidence of clinically significant sexual dysfunction. This can include a decrease in sexual desire, arousal difficulties, orgasmic dysfunction, or sexual pain disorders. It is important to note that the sexual dysfunction should have started during or soon after substance use or medication initiation.
Second, there must be evidence that the substance or medication is capable of causing sexual dysfunction. This can be determined by the timing of the sexual dysfunction in relation to substance use or medication initiation, as well as by the presence of other adverse effects associated with the substance or medication.
Distinguishing Factors
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be distinguished from other sexual dysfunctions by its temporal relationship to substance use or medication initiation. Unlike other sexual dysfunctions, substance-induced sexual dysfunction is typically reversible and improves with abstinence from the substance or discontinuation of the medication. This distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
It’s also important to consider the specific substance or medication involved. Different substances can have varying effects on sexual functioning. For example, substances such as alcohol, opioids, and sedatives can depress sexual desire and impair sexual performance. Stimulants, on the other hand, may increase sexual desire but can lead to difficulties with arousal or orgasm.
Specifiers
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction can be further specified based on the severity and duration of the symptoms. Severity can range from mild to moderate to severe, depending on the impact on sexual functioning and overall distress. Duration can be specified as acute (less than six months) or persistent (six months or more).
Specific Substances
Various substances and medications have been associated with sexual dysfunction. Alcohol, opioids, sedatives, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antihypertensive medications are among the most common culprits. It’s important to note that not everyone who uses these substances or medications will experience sexual dysfunction, but it is a potential side effect that should be considered.
Treatments
The treatment of substance-induced sexual dysfunction involves addressing both the underlying substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself. The primary approach is to promote abstinence from the substance or switch to an alternative medication that is less likely to cause sexual dysfunction.
In addition to addressing the substance or medication, various therapies can be helpful in managing sexual dysfunction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thoughts and beliefs related to sexual performance. Couples therapy can improve communication and intimacy, which can positively impact sexual functioning. In some cases, medication such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra) may be prescribed to temporarily alleviate sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
Substance-induced sexual dysfunction is a significant concern for individuals who use substances or take certain medications. Understanding the diagnostic features, distinguishing factors, and treatment options can help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage this condition. By addressing both the substance use or medication and the sexual dysfunction itself, individuals can work towards improving their sexual functioning and overall well-being.
Learn More
Understanding Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder (GPPPD) is a condition that affects individuals, predominantly women, and can have a significant impact on their sexual well-being and overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for GPPPD.
Causes of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
GPPPD can have various underlying causes, both physical and psychological. Physical causes may include vaginal infections, hormonal imbalances, pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, or certain medical conditions. Psychological factors such as anxiety, fear, past traumatic experiences, or relationship issues can also contribute to the development of GPPPD.
Symptoms of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
The symptoms of GPPPD can manifest differently in each individual, but common symptoms include pain or discomfort during vaginal penetration, muscle spasms in the pelvic floor, fear or anxiety related to sexual activities, and avoidance of sexual intimacy. These symptoms can have a significant impact on sexual satisfaction and overall well-being.
Diagnosis of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
Diagnosing GPPPD requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, conduct a physical examination, and may recommend additional tests or consultations with specialists to rule out any underlying physical or psychological conditions. It is essential to establish an accurate diagnosis to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment of Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder
Treating GPPPD often involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing both physical and psychological aspects of the condition. The treatment plan may include general measures, psychological therapies, or a combination of both.
General Measures
General measures aim to alleviate physical symptoms and promote overall sexual well-being. These may include:
– Lubricants: Using water-based lubricants during sexual activities can help reduce discomfort and improve sexual pleasure.
– Pelvic floor exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises, such as Kegels, can help improve muscle control and reduce pain.
– Education and counseling: Learning about GPPPD and receiving counseling can help individuals better understand their condition and develop coping strategies.
Psychological Therapies
Psychological therapies play a crucial role in addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of GPPPD. These therapies may include:
– Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs related to their condition, promoting healthier attitudes towards sex and intimacy.
– Mindfulness-based techniques: Techniques such as meditation and mindfulness can help individuals develop awareness and acceptance of their physical sensations, reducing anxiety and fear during sexual activities.
– Couples therapy: In cases where GPPPD affects the individual’s relationship, couples therapy can help improve communication, address relationship issues, and foster a supportive and understanding environment.
Conclusion
Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s sexual well-being and overall quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for GPPPD, individuals can seek appropriate help and support. With the right interventions, it is possible to manage and overcome GPPPD, leading to a healthier and more satisfying sexual life.
Learn More
Understanding Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction
Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder (FSIAD) is a condition that affects many women around the world. It is characterized by a persistent lack of sexual interest or arousal, leading to distress or difficulties in intimate relationships. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of FSIAD, providing a comprehensive understanding of this disorder.
Signs and Symptoms of Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder
The symptoms of FSIAD may vary from person to person, but commonly include:
1. Lack of interest in sexual activities
2. Reduced or absent sexual thoughts or fantasies
3. Difficulty in becoming sexually aroused, even in the presence of adequate stimulation
4. Lack of pleasure or satisfaction during sexual activities
5. Feelings of distress or frustration due to these difficulties
It is important to note that these symptoms should persist for a significant period of time, typically around six months, to be diagnosed as FSIAD.
Causes of Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder
The exact causes of FSIAD are not yet fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. These include:
1. Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, depression, past trauma, body image issues, and relationship problems can all impact a woman’s sexual interest and arousal.
2. Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during menopause or after childbirth, can affect sexual desire and arousal.
3. Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic pain, can also contribute to FSIAD.
4. Medications: Some medications, including antidepressants and certain blood pressure medications, may have side effects that affect sexual interest and arousal.
How Is Female Sexual Arousal and Interest Disorder Diagnosed?
To diagnose FSIAD, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough assessment, which may include:
1. Medical history: Gathering information about any underlying medical conditions, medications, or psychological factors that may be contributing to the symptoms.
2. Physical examination: A physical examination may be conducted to rule out any physical causes of the symptoms.
3. Psychological evaluation: Assessing for any psychological factors that may be impacting sexual interest and arousal.
4. Laboratory tests: In some cases, blood tests may be conducted to check hormone levels or rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Treatment and Medication Options for Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder (FSIAD)
The treatment of FSIAD typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing both physical and psychological factors. Some common treatment options include:
1. Psychotherapy: Individual or couples therapy can help address underlying psychological issues and improve sexual functioning.
2. Hormone therapy: In cases where hormonal imbalances are contributing to FSIAD, hormone replacement therapy may be recommended.
3. Medications: Certain medications, such as Addyi (flibanserin), have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of FSIAD. These medications work by targeting neurotransmitters in the brain to enhance sexual desire.
4. Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, stress management techniques, and improving communication in relationships, can also be beneficial.
Conclusion
Female Sexual Interest and Arousal Disorder can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life and intimate relationships. By understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of FSIAD, individuals can seek appropriate help and support. It is important to remember that FSIAD is a treatable condition, and with the right interventions, women can regain their sexual interest and arousal, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling sexual life.
Learn More
Understanding Premature Ejaculation: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is a common sexual dysfunction that affects many men. It is characterized by the inability to control or delay ejaculation, leading to unsatisfactory sexual experiences for both partners. The condition can cause distress and frustration, impacting the overall quality of life and intimate relationships.
How Common is Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is more common than you might think. Studies suggest that it affects approximately 1 in 3 men at some point in their lives. It can occur in men of all ages and backgrounds, and it is not limited to any specific demographic.
What Time Frame Medically Defines a Man’s Ejaculation as Premature?
Medically, premature ejaculation is defined as ejaculation that consistently occurs within one minute of penetration or before the individual desires it. However, it is important to note that the time frame may vary from person to person, and what is considered premature for one individual may not be the same for another.
What Causes Premature Ejaculation?
The exact cause of premature ejaculation is not fully understood. It is believed to be a combination of psychological and biological factors. Psychological causes may include anxiety, stress, performance anxiety, relationship issues, or a history of sexual trauma. Biological factors can include abnormal hormone levels, genetic predisposition, or an imbalance of neurotransmitters in the brain.
Are There Other Symptoms of Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is primarily characterized by the inability to control ejaculation, but it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
– Feelings of guilt, embarrassment, or frustration
– Decreased sexual satisfaction for both partners
– Avoidance of sexual intimacy
– Relationship difficulties
How are the Causes of Premature Ejaculation Diagnosed?
Diagnosing the causes of premature ejaculation involves a comprehensive evaluation of both physical and psychological factors. A healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough medical history review and may ask questions about sexual experiences, relationships, and any underlying health conditions. It is important to be open and honest during this process to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Are Lab Tests Needed to Make the Diagnosis of Premature Ejaculation?
In most cases, lab tests are not required to diagnose premature ejaculation. The diagnosis is primarily based on the individual’s medical history and the symptoms presented. However, in some instances, a healthcare professional may recommend additional tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions contributing to the problem.
How is Premature Ejaculation Treated?
There are various treatment options available for premature ejaculation. These include:
– Behavioral techniques: Techniques such as the start-stop method, squeeze technique, or pelvic floor exercises can help improve control over ejaculation.
– Counseling or therapy: Psychological counseling can address any underlying psychological factors contributing to premature ejaculation and help improve sexual confidence and communication.
– Medications: Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed to delay ejaculation. However, these should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
– Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of behavioral techniques and medication may be recommended for optimal results.
Prevention
While it may not always be possible to prevent premature ejaculation, there are steps individuals can take to minimize the risk. These include:
– Communicating openly with your partner about sexual preferences and concerns.
– Practicing relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety and stress.
– Engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
– Seeking professional help if experiencing persistent difficulties.
Conclusion
Premature ejaculation is a common condition that can have a significant impact on a man’s sexual satisfaction and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for individuals seeking help. With the right support and guidance, premature ejaculation can be effectively managed, leading to improved sexual experiences and a healthier, more fulfilling intimate life.
Learn More
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Types, and Symptoms
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects men of all ages. It is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. ED can have a significant impact on a man’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall quality of life.
Types of Erectile Dysfunction
There are two main types of erectile dysfunction:
- Organic ED: This type of ED is caused by physical factors such as poor blood flow to the penis, nerve damage, or hormonal imbalances.
- Psychological ED: Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression, or relationship problems, can contribute to this type of ED.
How Common is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. According to studies, it is estimated that approximately 30 million men in the United States alone experience some form of erectile dysfunction. The prevalence of ED increases with age, but it can occur at any stage of life.
What is the Usual Age for Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction can affect men of all ages, but it becomes more common as men get older. It is estimated that around 40% of men in their 40s experience some degree of ED, while the percentage increases to 70% for men in their 70s. However, it is important to note that ED is not a normal part of aging and can be treated.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
The main symptom of erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection. Other symptoms may include:
- Reduced sexual desire
- Difficulty achieving orgasm
- Premature ejaculation
- Delayed ejaculation
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can have various causes, including:
- Certain conditions or diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, and Parkinson’s disease can contribute to ED.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications, can interfere with the ability to achieve or maintain an erection.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems can all play a role in the development of ED.
Conclusion
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that can have a significant impact on a man’s life. It is important to understand that ED is not a normal part of aging and can often be treated. If you are experiencing symptoms of erectile dysfunction, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can help identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Learn More
Understanding Delayed Ejaculation: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is Delayed Ejaculation?
Delayed ejaculation is a sexual disorder characterized by the inability or significant delay in achieving ejaculation, despite sufficient sexual stimulation. It is a condition that affects men and can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction in sexual relationships.
Who does Delayed Ejaculation Affect?
Delayed ejaculation can affect men of all ages, although it is more commonly observed in older men. It is estimated that around 1-4% of men experience delayed ejaculation at some point in their lives.
How Common is Delayed Ejaculation?
Delayed ejaculation is considered a relatively uncommon sexual disorder. However, due to underreporting and the sensitive nature of the topic, the actual prevalence may be higher than reported.
What are the Symptoms of Delayed Ejaculation?
The main symptom of delayed ejaculation is the persistent delay or inability to ejaculate, even with prolonged sexual stimulation. Men with delayed ejaculation may experience frustration, anxiety, and reduced sexual satisfaction. It is important to note that occasional instances of delayed ejaculation are not necessarily indicative of the disorder.
What Causes Delayed Ejaculation?
Delayed ejaculation can have both psychological and physical causes. Psychological factors such as anxiety, stress, relationship issues, or past traumatic experiences can contribute to the condition. Certain medications, nerve damage, hormonal imbalances, or prostate-related issues may also play a role in causing delayed ejaculation.
How is Delayed Ejaculation Diagnosed?
To diagnose delayed ejaculation, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough medical history and physical examination. They may also inquire about sexual habits, relationships, and any underlying psychological factors. In some cases, laboratory tests or specialized assessments may be recommended to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
How is Delayed Ejaculation Treated?
The treatment for delayed ejaculation depends on the underlying cause. In cases where psychological factors are involved, therapy or counseling may be recommended to address any underlying issues. Behavioral techniques, such as the “stop-start” or “squeeze” methods, may also be employed to help improve ejaculatory control. In some instances, medications or hormone therapy may be prescribed to address any physical factors contributing to the condition.
Are There Exercises That Will Help with Delayed Ejaculation?
Yes, there are exercises that can potentially help with delayed ejaculation. Kegel exercises, which involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles, may be beneficial in improving ejaculatory control. These exercises can be practiced regularly to strengthen the muscles involved in ejaculation.
How Can I Prevent Delayed Ejaculation?
Preventing delayed ejaculation involves addressing any underlying psychological or physical factors that may contribute to the condition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking therapy or counseling when necessary can all play a role in preventing or managing delayed ejaculation.
Conclusion
Delayed ejaculation is a sexual disorder that can cause frustration and dissatisfaction in men. It is important to understand that delayed ejaculation can have both psychological and physical causes, and treatment options may vary based on the underlying factors. Seeking professional help and open communication with partners can greatly contribute to managing and overcoming delayed ejaculation. Remember, it is a treatable condition, and with the right approach, sexual satisfaction can be restored.
Learn More
Suicide Prevention: Understanding and Taking Action
When it comes to suicide prevention, knowledge and action are key aspects. Suicide is a serious public health issue that affects individuals, families, and communities worldwide. It is important to understand the signs and risk factors associated with suicide, as well as the steps we can take to prevent it.
One of the most important things we can do is to be aware of the warning signs of suicide. These can include talking about wanting to die or feeling hopeless, withdrawing from friends and family, giving away belongings, or displaying sudden changes in mood or behavior. If you notice any of these signs in yourself or someone you know, it is crucial to take them seriously and seek help.
Preventing suicide requires a multi-faceted approach. It involves creating a supportive environment, promoting mental health and well-being, and providing access to effective treatment and support services. It is important to reach out to those who may be struggling and offer them a listening ear, empathy, and resources for help.
If you or someone you know is in crisis, it is important to seek immediate help. There are several helpline numbers and crisis intervention services available that can provide support and guidance. Remember, you are not alone, and there is help available.
- Take Water. Just try to recollect the beautiful moments in your life.
- Just bring the image of those who truly love you in your visualization. Think about them.
- Think about your good friends in large.
- Talk to your doctor or with anyone who is nearby. Share your feelings.
- Think about your Dreams and desires for a second.
- Listen to the videos given at the end of this write up.
- Please get in touch with anyone of these numbers which is nearer to you or helpful to you.
| LOCATION | ORGANISATION | NUMBER | HOURS OF OPERATION |
| ALL-INDIA | GOVT MH Rehabilitation HELPLINE ‘KIRAN’ | 1800-5990019 | 24/7 |
| ALL-INDIA | VANDREVALA FOUNDATION | 9999 666 555 | 24 by 7/ |
| E: help@vandrevalafoundation.com if you don’t get through and expect a call-back | |||
| BANGALORE | SAHAI | 080-25497777 | Monday – Saturday 10 AM to 5:30PM |
| CHENNAI | SNEHA | 044 2464 0050 | Daily: 8 AM to 10 PM |
| E: help@snehaindia.org | |||
| DELHI | SANJIVINI SOCIETY FOR MENTAL HEALTH | 01140769002, 01141092787 | Daily: 10 AM to 4 PM |
| 01124311918, 01124318883, 01143001456 | |||
| GANGTOK | SIKKIM HELPLINE NUMBER | 1800-3453225 | 24/7 |
| HYDERABAD | ONE LIFE | 78930 78930 | 24/7 |
| KOLKATA | |||
| LIFELINE FOUNDATION | +91 9088030303, 03340447437 | Daily 10 AM to 10 PM / Caters to pan-India calls | |
| E: contact@lifelinefoundation.in | |||
| Site: www.lifelinefoundation.in | |||
| MUMBAI | |||
| SAMARITANS | 84229 84528, 84229 84529, 84229 84530 | Daily 5 PM to 8 PM | |
| E: talk2samaritans@gmail.com |