Understanding Anger Management: History, Principles, and Benefits
Introduction
Anger is an intense emotional response that everyone experiences from time to time. While anger itself is a normal and natural emotion, it can become problematic when it is not managed effectively. This is where anger management comes into play. In this article, we will explore the history of anger management, the principles behind it, the various types of anger management techniques, and the benefits it can bring.
History of Anger Management
The concept of anger management can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Philosophers such as Aristotle and Seneca emphasized the importance of self-control and moderation in dealing with anger. However, it wasn’t until the 1970s that anger management became a recognized field of study.
What Anger Management Practitioners Do
Anger management practitioners are professionals who specialize in helping individuals identify and control their anger. They use a variety of techniques and strategies to assist their clients in managing their anger effectively. These may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, communication skills training, and stress management techniques.
Principles of Anger Management
Anger management is based on several key principles:
- Self-awareness: Recognizing the signs and triggers of anger.
- Self-control: Learning to respond to anger in a calm and controlled manner.
- Effective communication: Developing healthy ways to express anger and resolve conflicts.
- Stress management: Learning techniques to reduce stress and prevent anger from escalating.
Various Types of Anger Management
There are several different approaches to anger management, each tailored to suit individual needs:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): This approach focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anger.
- Relaxation techniques: These include deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation to help individuals calm their minds and bodies.
- Anger management classes: Group sessions that provide education, support, and practical skills for managing anger.
- Individual counseling: One-on-one sessions with a therapist who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Benefits of Anger Management
Anger management can have numerous benefits for individuals who struggle with anger-related issues:
- Better relationships: Learning to manage anger effectively can improve communication and reduce conflicts in personal and professional relationships.
- Improved mental health: Anger management techniques can help individuals reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Enhanced physical health: Uncontrolled anger can have negative effects on physical health, and managing anger can lead to better overall well-being.
- Increased self-awareness: Anger management helps individuals gain insight into their emotions and triggers, leading to greater self-awareness and personal growth.
Possible Treatments
When seeking help for anger management, it is essential to consult with a qualified professional who can assess the individual’s needs and recommend appropriate treatments. These may include therapy, counseling, support groups, or a combination of approaches tailored to the individual’s specific situation.
Conclusion
Anger management is a valuable tool for individuals who struggle with anger-related issues. By understanding the history, principles, and various types of anger management, individuals can gain control over their anger and improve their overall well-being. Seeking professional help and utilizing effective anger management techniques can lead to healthier relationships, improved mental health, and a more fulfilling life.
Learn More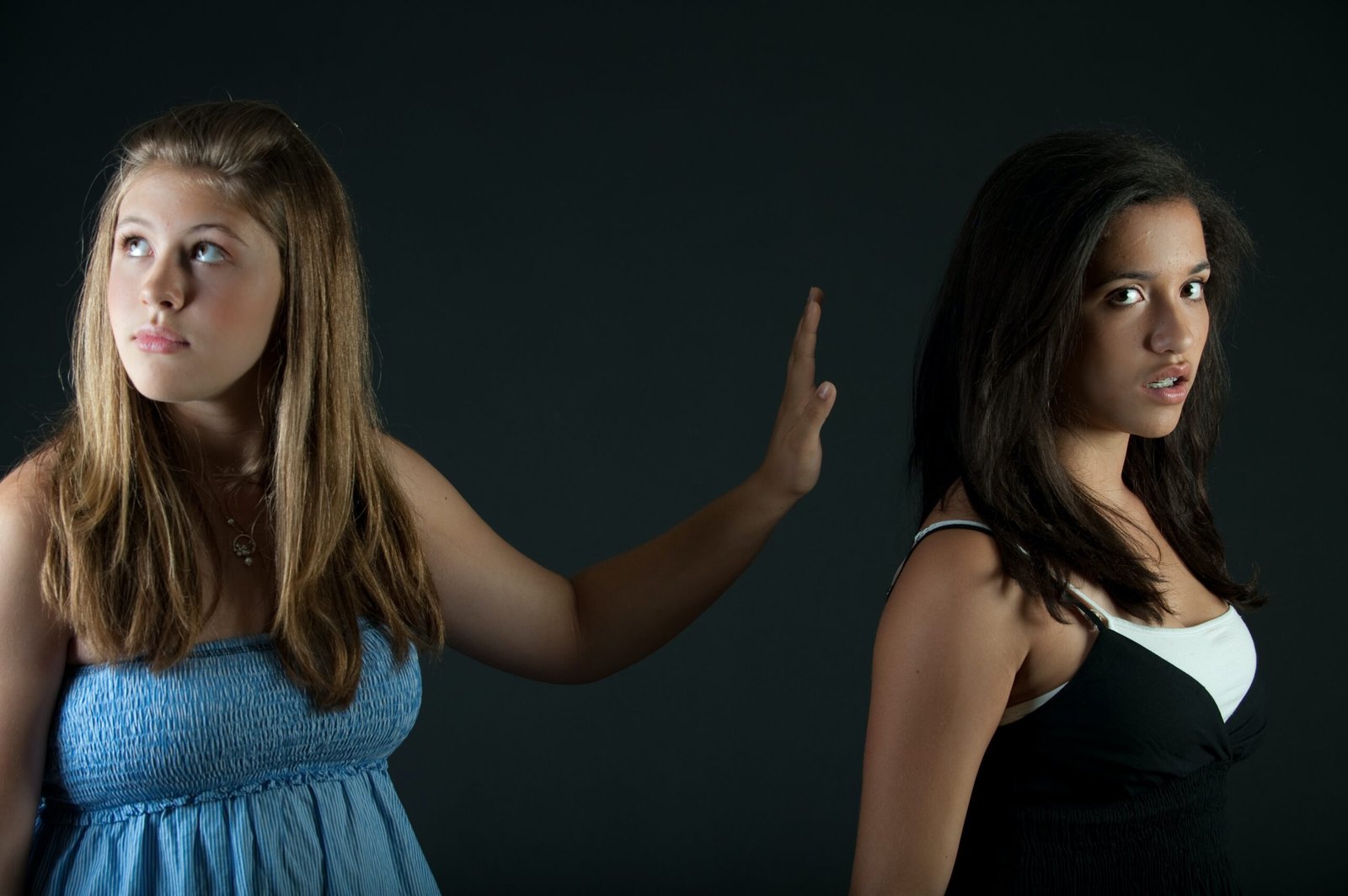
Steps to Overcoming Teenage Anger: Understanding the Causes, Effects, and Therapies
Introduction
Teenage anger is a common and natural emotion that arises during adolescence. However, when left unaddressed, it can have detrimental effects on both the individual and their relationships. In this article, we will explore the possible causes of teenage anger, its effects, and provide practical steps to help teenagers overcome their anger. Additionally, we will delve into various therapies that can be effective in managing and reducing anger in teenagers.
Possible Causes for Teenage Anger
Understanding the underlying causes of teenage anger is crucial in helping teenagers navigate through this challenging phase. Some possible causes of teenage anger include:
- Hormonal changes: Adolescence is a time of significant hormonal fluctuations, which can contribute to mood swings and heightened emotions.
- Stress and pressure: Academic demands, peer pressure, and expectations from family and society can all contribute to feelings of anger and frustration.
- Family issues: Conflict within the family, strained relationships, or unstable home environments can trigger anger in teenagers.
- Unresolved trauma or past experiences: Previous traumatic events or unresolved emotional issues can manifest as anger in teenagers.
The Effects of Teenage Anger
When anger is not effectively managed, it can have detrimental effects on various aspects of a teenager’s life, including:
- Physical health: Chronic anger can lead to increased stress levels, weakened immune system, and other physical health problems.
- Mental health: Unresolved anger can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and aggression.
- Social relationships: Frequent outbursts of anger can strain relationships with friends, family members, and peers, leading to isolation and feelings of loneliness.
- Academic performance: Anger can impair concentration, focus, and motivation, negatively impacting a teenager’s academic performance.
How to Help Teenagers When They are in Anger
Supporting teenagers in managing their anger requires patience, empathy, and effective communication. Here are some strategies to help teenagers when they are experiencing anger:
- Encourage open communication: Create a safe and non-judgmental space for teenagers to express their emotions and concerns.
- Teach anger management techniques: Help teenagers develop healthy coping mechanisms such as deep breathing exercises, journaling, or engaging in physical activities.
- Model healthy behavior: Set a positive example by managing your own anger in a constructive manner.
- Validate their feelings: Acknowledge and validate the teenager’s emotions, letting them know that their feelings are valid and understood.
- Seek professional help if necessary: If anger issues persist or significantly impact a teenager’s daily life, it may be beneficial to seek the guidance of a mental health professional.
Therapies for Teenage Anger
Various therapeutic approaches can be effective in helping teenagers manage and reduce their anger:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps teenagers identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier ways of coping with anger.
- Expressive therapies: Art therapy, music therapy, or dance therapy can provide teenagers with alternative outlets to express and process their anger.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help teenagers cultivate self-awareness and regulate their emotions.
- Family therapy: Involving the entire family in therapy can address underlying family dynamics and promote healthier communication and conflict resolution strategies.
- Support groups: Connecting with peers who are experiencing similar challenges can provide teenagers with a sense of belonging and support.
Conclusion
Teenage anger is a complex emotion that requires understanding, patience, and effective strategies for management. By identifying the possible causes, recognizing the effects, and implementing appropriate therapies, we can support teenagers in overcoming their anger and fostering healthier emotional well-being. Remember, seeking professional help when necessary is always a valuable option in ensuring the best possible outcomes for teenagers dealing with anger-related issues.
Learn More