
Understanding CBT and Core Beliefs: Types and Examples
What is CBT?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is a goal-oriented and evidence-based approach that helps individuals identify and change unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior.
What is a Core Belief in CBT?
In CBT, core beliefs are deeply ingrained beliefs that individuals hold about themselves, others, and the world around them. These beliefs are often formed during childhood and can shape our perceptions, emotions, and actions. Core beliefs are considered to be the lens through which individuals interpret and make sense of their experiences.
Types of Core Beliefs in CBT
There are three types of core beliefs commonly identified in CBT:
- Core Beliefs about the Self: These beliefs relate to one’s worth, abilities, and identity. Examples include “I am unworthy,” “I am incompetent,” or “I am unlovable.”
- Core Beliefs about Others: These beliefs pertain to how individuals perceive and interact with others. Examples include “People are untrustworthy,” “Others will always reject me,” or “People are out to get me.”
- Core Beliefs about the World: These beliefs involve one’s views on the world and their place in it. Examples include “The world is a dangerous place,” “Life is unfair,” or “Nothing ever goes right for me.”
Examples of Negative Core Beliefs
Here are 20 examples of negative core beliefs:
- I am worthless.
- I am a failure.
- I am unlovable.
- I am stupid.
- I am always to blame.
- Others will abandon me.
- People are out to get me.
- I will never be successful.
- I am a burden to others.
- I am not good enough.
- People will always betray me.
- I am powerless.
- I am fundamentally flawed.
- Nothing I do matters.
- I am always rejected.
- I don’t deserve happiness.
- I am a disappointment.
- I will never be happy.
- Life is meaningless.
- I am always alone.
What are Automatic Negative Thoughts?
Automatic Negative Thoughts (ANTs) are the spontaneous and often unconscious thoughts that arise in response to specific situations or triggers. These thoughts are typically negative and can contribute to negative emotions and behaviors. ANTs are a key focus in CBT as they play a significant role in maintaining negative core beliefs and perpetuating unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior.
Examples of Automatic Negative Thoughts
Here are 20 examples of automatic negative thoughts:
- This always happens to me.
- I can’t do anything right.
- Everyone is judging me.
- I will never be good enough.
- I’m a failure.
- Nothing ever goes my way.
- I’m so stupid.
- I’ll never be able to change.
- I’m always to blame.
- It’s too hard, I can’t handle it.
- I’m worthless.
- Everyone is against me.
- I’m a burden to others.
- I’ll never succeed.
- I’m always alone.
- I’m a disappointment to everyone.
- I don’t deserve happiness.
- I’ll never be happy.
- Nothing matters.
- It’s always my fault.
Understanding core beliefs and automatic negative thoughts is crucial in CBT as it allows individuals to challenge and replace these unhelpful patterns of thinking with more realistic and positive alternatives. By doing so, individuals can improve their emotional well-being and develop healthier coping strategies.
Related Posts
Understanding CBT and Core Beliefs: Types and Examples
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AhTdAU4LV6g What is CBT?Cognitive Behavioral...
What is CBT? A Comprehensive Guide to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
-CLICK HERE TO LISTEN-NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CBT - AUDIO SELF -HELP SERIES...
Understanding Cognitive Behaviour Therapy and the Principle of Goal Orientation and Problem Focus
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u3aBwGxTtSE Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is...
Accelerated Experiential Dynamic Psychotherapy: An Effective Approach to Emotional Healing
Introduction Accelerated Experiential Dynamic Psychotherapy (AEDP) is a...




Hare Krishna,
CBT is a widely recognized form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connection between our thoughts, feelings and behavior. It is goal oriented and evidence based approach that that helps individuals identify and change unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior.
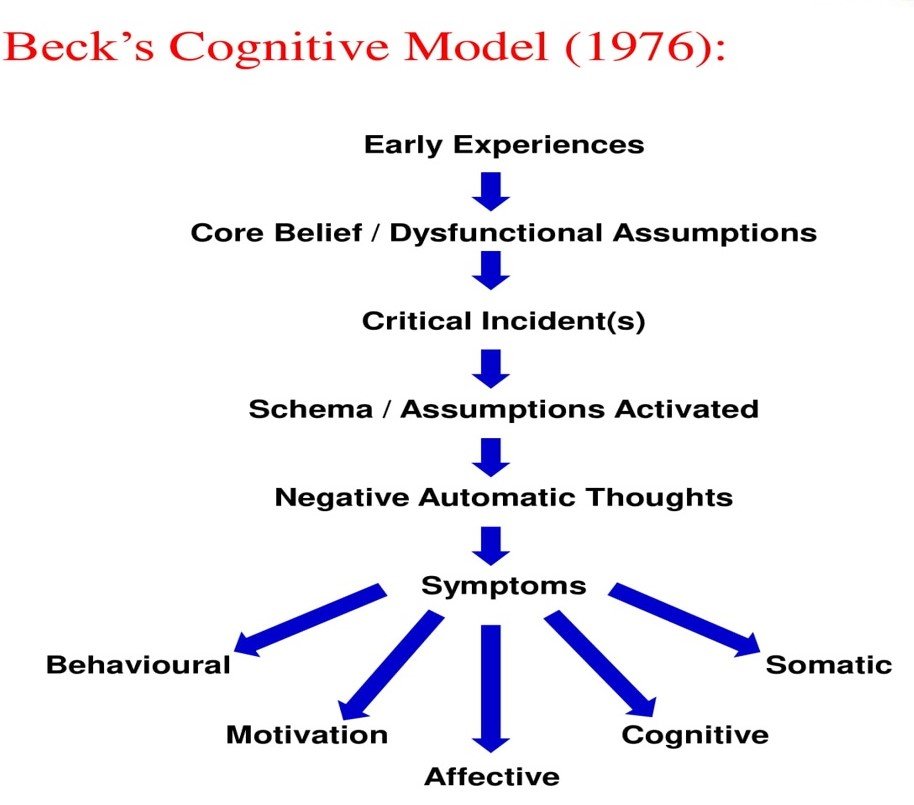
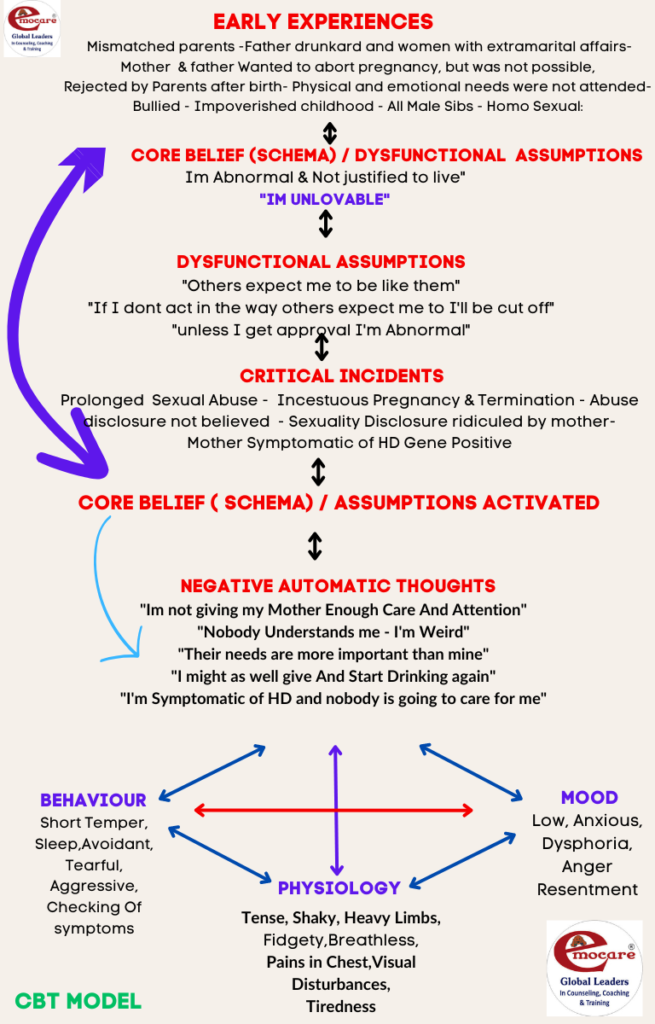
Beck’s cognitive model (1976) explains to us that early experiences create core beliefs also known as schema/dysfunctional assumptions. When critical incident or
critical incidents occur in life, core beliefs, schema,dysfunctional assumptions get activated and automatic negative thoughts are aroused as a consequence which manifests in the form of symptoms visualized in our behavior, thoughts, motivations, emotional component known as effective component and somatic component.
Hare Krishna, CBT is goal oriented and problem focused therapy. It doesn’t delve into past but rather it focuses on present and future.
In CBT goals are structured around smart framework. S designates specific goals. M designates measurable goals. A designates achievable goals. R designates Relevant goals and T designates Time bound Goals. Goals are evaluated, revised, challenged and purpose of CBT is to identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior. CBT provides individuals with practical tools and strategies to overcome current problems and improve their overall well being