
Understanding Cognitive Behaviour Therapy and Symptoms of PTSD
What is Cognitive Behaviour Therapy?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected, and that by changing our thoughts, we can change our emotions and actions.
What is the Beck Model?
The Beck Model, developed by Aaron Beck, is a cognitive therapy approach that aims to help individuals identify and modify their automatic negative thoughts. It is commonly used in CBT to treat various mental health conditions, including Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).

ptsd-symptoms
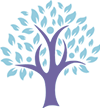
Symptoms created by automatic negative thoughts in PTSD
Individuals suffering from PTSD often experience a range of symptoms resulting from automatic negative thoughts triggered by traumatic events. These symptoms can include:
- Recurrent intrusive thoughts or memories
- Nightmares or flashbacks
- Intense distress or physiological reactions when exposed to triggers
- Avoidance of reminders of the traumatic event
- Negative changes in mood or cognition
- Hyperarousal or hypervigilance
Behavioural symptoms in PTSD
Behavioural symptoms in PTSD can manifest as avoidance of certain places, people, or activities associated with the traumatic event. Individuals may also exhibit changes in their sleep patterns, irritability, or aggressive behavior.
Motivation in PTSD
In PTSD, motivation can be affected due to the negative impact of the traumatic event on an individual’s thoughts and emotions. They may experience a lack of interest or pleasure in activities they once enjoyed, as well as a decreased drive to engage in daily tasks or pursue goals.
Affective symptoms in PTSD
Affective symptoms in PTSD refer to the emotional changes experienced by individuals. These can include feelings of sadness, guilt, shame, anger, fear, or a sense of emotional numbness. Mood swings and difficulty experiencing positive emotions may also be present.
Cognitive symptoms in PTSD
Cognitive symptoms in PTSD involve changes in thinking patterns. This can include negative self-perceptions, distorted beliefs about oneself or the world, difficulty concentrating or remembering details of the traumatic event, and excessive worry or rumination.
Somatic symptoms in PTSD
Somatic symptoms in PTSD are physical manifestations of the condition. These can include headaches, stomachaches, muscle tension, fatigue, changes in appetite or weight, and other physical discomforts that may arise as a result of the traumatic experience.
In conclusion, Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and the Beck Model offer effective approaches for addressing the symptoms of PTSD. By targeting negative thoughts and behaviors, individuals can work towards managing and overcoming the challenges associated with this condition.
Related Posts
The Power of Visualization Exercises: A Guide to Progressive Muscle Visualization
Introduction Visualization exercises are a powerful tool for improving mental...
The Importance of Mental Health in Children
Introduction Mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and this...
Understanding Anxiety Disorders According to DSM-5-TR
What is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5-TR? The...
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Principles
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cLYRV29mflM What is CBT? Cognitive Behavioral...





Hare Krishna,
CBT and Beck model offer effective approaches for addressing the symptoms of PTSD.
PTSD is manifested by cognitive symptoms, somatic symptoms, behavioral symptoms, affective symptoms and decreased motivation in daily tasks and in activities once enjoyed.
Cognitive symptoms comprise of faulty perception of self,world,difficulty concentrating,excessive worry and rumination. There are changes in the thinking patterns.
Somatic symptoms are manifested in form of headache, stomach ache,fatigue, changes in appetite and weight.
Behavioral symptoms manifest in the form of avoiding people, places,activities associated with the traumatic event.
Affective symptoms manifest in the form of guilt, shame,anger,sadness, fear,or a sense of emotional numbness. Mood swings and difficulty experiencing positive symptoms may be present.
Hare Krishna,
Conduct disorder is a mental health condition characterized by persistent pattern of behavior that violates the basic rights of others or societal norms. It takes place in childhood or adolescence and can have significant social, emotional and academic consequences.
Symptoms include aggression towards people or animals, destruction of property, deceitfulness or theft,violation of rules or law,lack of empathy or remorse.
Its subcategories include: a)childhood onset.b)adolescent onset.c)unspecified onset d)with limited prosocial emotions.
Hare Krishna,
Counseling is a professional helping relationship between a counselor and client (counselee)wherein counselor helps the counselee overcome their personal, emotional and psychological issues. Counseling is a short term therapeutic process which is usually done for mild cases like stress management, relationship issues, and mild emotional problems.various types of counseling are there like cbt,psychodynamic therapy, humanistic therapy and family therapy. Steps involved in counseling are assessment,goal setting,exploration,intervention and evaluation. Counseling can be directive or non directive.
Self counseling can be done by self reflection, self care practices, seeking support and self help resources.
Psychotherapy is long term process which is done for severe cases like traumatic cases,severe emotional problems, personality disorder etc.
Hare Krishna,
Anxiety is a natural response to stress or danger. It is a feeling of fear or apprehension about what is to come.
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent fear,worry and unease which are beyond the normal feelings of nervousness or stress and can interfere with a person’s ability to function.
Various anxiety disorders are generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social phobia, specific phobia, OCD,PTSD etc.
Treatment modality of anxiety disorders are antidepressants,antianxiety drugs,beta blockers, CBT,Lifestyle changes,self help strategies like mindfulness, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, breathing exercises, journaling, indulgence in hobbies, regular exercise, establishing a consistent sleep routine, limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption etc.
Causes of anxiety disorders include genetic factors, brain chemistry, environmental factors, personality traits etc
Hare Krishna,
Gender dysphoria spectrum is defined by DSM5 TR variety of experiences where individuals may feel a disconnect between the assigned gender at birth and gender identity.
Symptoms of gender dysphoria spectrum disorder include strong and persistent feelings of discomfort or distress related to one’s assigned gender. A desire to be treated as different gender,a preference for clothing, activities or roles typically associated with the opposite gender, a strong desire to alter one’s physical appearance to align with their gender identity, significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.