Understanding the Cognitive Triad in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Introduction
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective therapeutic approach that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. One of the key concepts in CBT is the Cognitive Triad, which refers to the three core areas of negative thinking: self, world, and future. In this blog post, we will explore what the Cognitive Triad is and provide examples of negative views within each area. We will also discuss how the Cognitive Triad can be used in counseling.
The Cognitive Triad
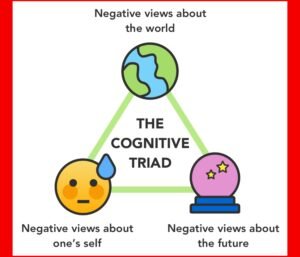
The Cognitive Triad is a framework developed by Aaron Beck, the founder of CBT. It suggests that individuals who experience emotional distress often have negative views about themselves, the world, and the future. These negative views can contribute to feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. By identifying and challenging these negative thoughts, individuals can develop more positive and realistic beliefs.
CBT COGNITIVE TRIAD
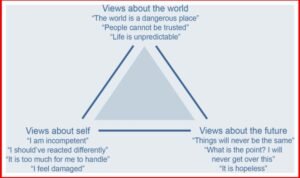
Examples of Negative Views about Self in the Cognitive Triad
1. “I am worthless and incapable.”
2. “I always mess things up.”
3. “Nobody likes me, and I’m unlovable.”
4. “I am a failure in everything I do.”
5. “I am a burden to others.”
6. “I am not good enough.”
7. “I will never succeed in life.”
8. “I am ugly and unattractive.”
9. “I am a disappointment to my family.”
10. “I am a complete failure as a person.”
COGNITIVE TRIAD
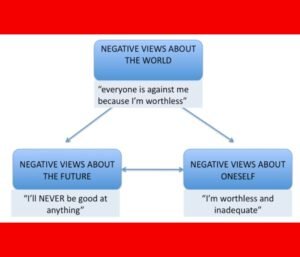
Examples of Negative Views about the World in the Cognitive Triad
1. “The world is a dangerous and hostile place.”
2. “Nobody can be trusted.”
3. “Everyone is out to get me.”
4. “The world is unfair and unjust.”
5. “Nothing good ever happens to me.”
6. “People are always judging me.”
7. “I will never find happiness or fulfillment.”
8. “The world is full of pain and suffering.”
9. “I am always surrounded by negativity.”
10. “The world is a hopeless and depressing place.”
COGNTIVE TRIAD-EMOCARE
Examples of Negative Views about the Future in the Cognitive Triad
1. “I will never achieve my goals.”
2. “Things will never get better for me.”
3. “I will always be stuck in this situation.”
4. “There is no point in trying because I will fail anyway.”
5. “I have no control over what happens to me.”
6. “The future is bleak and hopeless.”
7. “I will never be happy or fulfilled.”
8. “I will always be alone and lonely.”
9. “I will never overcome my challenges.”
10. “The future holds nothing but disappointment and pain.”
Using the Cognitive Triad in Counseling
Counselors and therapists trained in CBT can utilize the Cognitive Triad to help individuals challenge and reframe their negative thoughts. Here are some steps to effectively use the Cognitive Triad in counseling:
1. Identify negative thoughts
Encourage the individual to become aware of their negative thoughts about themselves, the world, and the future. This can be done through open-ended questions and active listening.
2. Challenge negative thoughts
Guide the individual in examining the evidence for and against their negative thoughts. Help them identify any cognitive distortions or biases in their thinking. Encourage them to consider alternative perspectives.
3. Reframe negative thoughts
Assist the individual in replacing their negative thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones. Help them find evidence that supports a more positive or neutral outlook. Encourage them to consider different possibilities and outcomes.
4. Practice new thought patterns
Support the individual in practicing their new thought patterns outside of therapy sessions. Encourage them to challenge negative thoughts as they arise and replace them with healthier alternatives. Provide guidance on coping strategies and self-care.
5. Monitor progress
Regularly assess and monitor the individual’s progress in challenging and reframing their negative thoughts. Celebrate small victories and provide encouragement and support throughout the process.
Conclusion
The Cognitive Triad is a valuable framework within CBT that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts about themselves, the world, and the future. By addressing and replacing these negative beliefs, individuals can experience improved emotional well-being and develop a more positive outlook on life. In counseling, the Cognitive Triad serves as a powerful tool for therapists to guide clients towards positive change and personal growth.
Remember, if you or someone you know is struggling with negative thoughts and emotions, seeking the help of a trained mental health professional can make a significant difference in promoting well-being and improving overall quality of life.
Related Posts
Understanding Depression: Symptoms, Differences, and Treatment Options
Introduction Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions...
Understanding Gender Dysphoria Spectrum: A Guide to DSM-5-TR
Introduction The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth...
Understanding Anxiety Disorders According to DSM-5-TR
What is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5-TR? The...
Exploring the World of Art Therapy: Benefits, Treatments, and Self-Care
Introduction Art therapy is a form of psychotherapy that utilizes the creative...