
Understanding the Hot-Cross Bun Model in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
In the realm of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), the Hot-Cross Bun Model is a valuable tool that helps individuals understand the intricate relationship between their thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors. This model provides a comprehensive framework for therapists and clients to explore the interconnected nature of these components and identify patterns that contribute to distressing or unhelpful experiences.
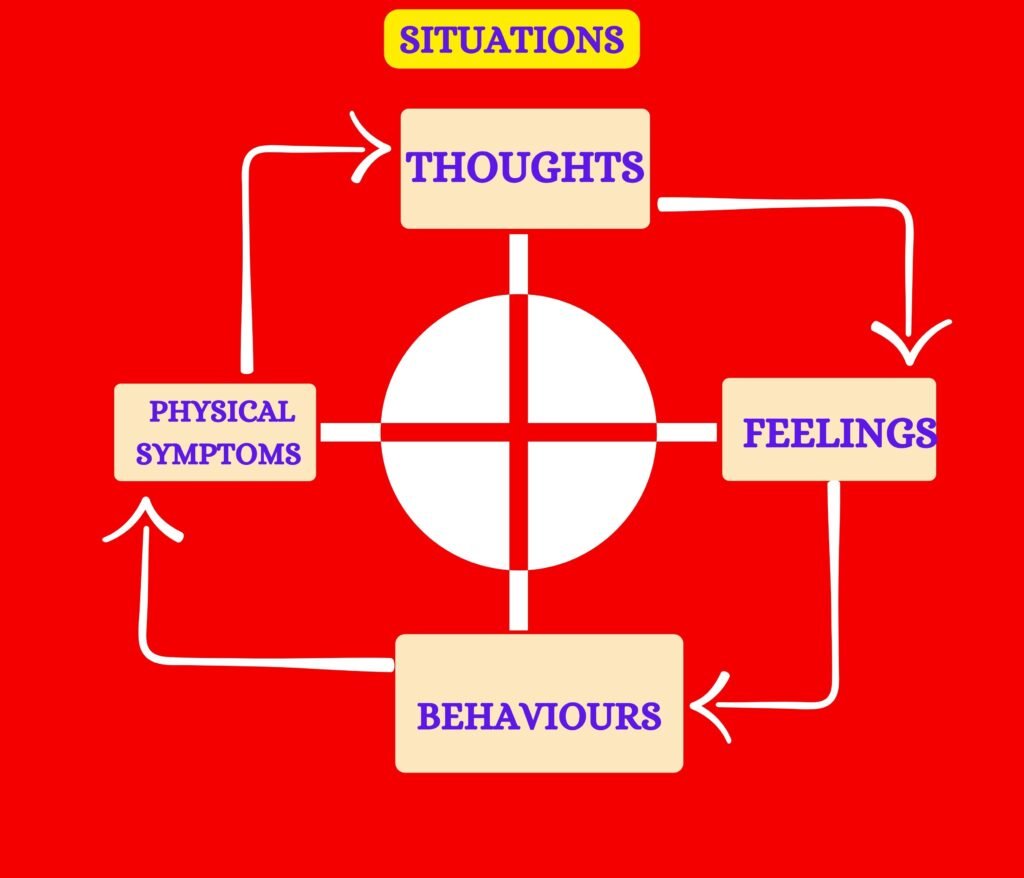
Hot cross-bun model of cbt
Exploring the Hot-Cross Bun Model
The Hot-Cross Bun Model consists of four interconnected components:
- Thoughts: Our thoughts are the ideas, beliefs, and interpretations we have about ourselves, others, and the world around us. These thoughts can be conscious or unconscious and greatly influence our emotions and behaviors.
- Emotions: Emotions are our subjective experiences that arise in response to certain situations or thoughts. They can range from positive emotions like joy and excitement to negative emotions such as sadness, anger, or anxiety.
- Physical Sensations: Physical sensations refer to the bodily experiences that accompany our thoughts and emotions. These sensations can manifest as tension, butterflies in the stomach, rapid heartbeat, sweating, or any other physiological response.
- Behaviors: Behaviors encompass the actions we take in response to our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations. These actions can be overt or covert, and they play a crucial role in shaping our experiences and interactions with the world.
The Hot-Cross Bun Model illustrates that these four components are interconnected and influence each other in a circular manner. Changes in one component can lead to changes in others, creating a feedback loop that can either maintain distress or contribute to positive change.
Example 1: Social Anxiety
Let’s consider an example to better understand the Hot-Cross Bun Model. Sarah experiences social anxiety and often avoids social situations. Using the model, we can explore the connections between her thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors:
- Thoughts: Sarah frequently thinks, “I’m going to embarrass myself,” or “People will judge me.” These thoughts contribute to her anxiety and avoidance of social situations.
- Emotions: Sarah experiences intense anxiety, fear, and self-consciousness when faced with social interactions.
- Physical Sensations: Sarah’s physical sensations include a racing heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and stomach discomfort.
- Behaviors: As a result of her thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations, Sarah avoids social situations, cancels plans, or leaves early to alleviate her anxiety.
This example demonstrates how Sarah’s thoughts about being judged or embarrassed lead to intense anxiety, which triggers physical sensations. In response, she engages in avoidance behaviors, perpetuating the cycle of social anxiety.
Example 2: Depression
Another example can help illustrate the Hot-Cross Bun Model in the context of depression:
- Thoughts: John often thinks, “I’m worthless,” or “Nothing ever goes right for me.” These negative thoughts contribute to his feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
- Emotions: John experiences persistent sadness, lack of motivation, and a sense of despair.
- Physical Sensations: John’s physical sensations include low energy, changes in appetite, disrupted sleep patterns, and general body aches.
- Behaviors: Due to his thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations, John withdraws from social activities, neglects self-care, and has difficulty concentrating on tasks.
In this example, John’s negative thoughts about his worth and the belief that nothing will improve contribute to his feelings of sadness. These emotions, in turn, manifest as physical sensations and lead to behaviors that reinforce his depressive state.
Using the Hot-Cross Bun Model in Therapy
The Hot-Cross Bun Model serves as a valuable tool in CBT therapy sessions. Therapists and clients can use this model to identify and challenge unhelpful thoughts, explore the emotional and physical responses associated with those thoughts, and develop strategies to modify behaviors that maintain distress.
By understanding the interconnected nature of thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors, individuals can gain insight into the factors contributing to their difficulties and work towards making positive changes.
Remember, the Hot-Cross Bun Model is just one of many tools used in CBT, and its application may vary depending on individual circumstances. A qualified therapist can guide clients through this model and tailor interventions to their specific needs.
Overall, the Hot-Cross Bun Model provides a clear visual representation of the complex interplay between thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors. By examining these components, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their experiences and take steps towards improving their well-being.
Related Posts
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Automatic Negative Thoughts
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IQa0nKsojs0Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is...
Understanding the Hot-Cross Bun Model in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hd2ntZYAYfA In the realm of Cognitive Behavioral...
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Its Origins
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized form of therapy that...
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Automatic Negative Thoughts
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely-used therapeutic approach that...


The interconnected nature of thoughts, emotions, behaviour and physical sensations.